Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction 2. Data
3. Measuring Media Slant and 3.1. Text pre-processing and featurization
3.2. Classifying transcripts by TV source
3.3. Text similarity between newspapers and TV stations and 3.4. Topic model
4. Econometric Framework
4.1. Instrumental variables specification
4.2. Instrument first stage and validity
5. Results
6. Mechanisms and Heterogeneity
6.1. Local vs. national or international news content
6.2. Cable news media slant polarizes local newspapers
Online Appendices
A. Data Appendix
A.2. Alternative county matching of newspapers and A.3. Filtering of the article snippets
A.4. Included prime-time TV shows and A.5. Summary statistics
B. Methods Appendix, B.1. Text pre-processing and B.2. Bigrams most predictive for FNC or CNN/MSNBC
B.3. Human validation of NLP model
B.6. Topics from the newspaper-based LDA model
C. Results Appendix
C.1. First stage results and C.2. Instrument exogeneity
C.3. Placebo: Content similarity in 1995/96
C.8. Robustness: Historical circulation weights and C.9. Robustness: Relative circulation weights
C.12. Mechanisms: Language features and topics
C.13. Mechanisms: Descriptive Evidence on Demand Side
C.14. Mechanisms: Slant contagion and polarization
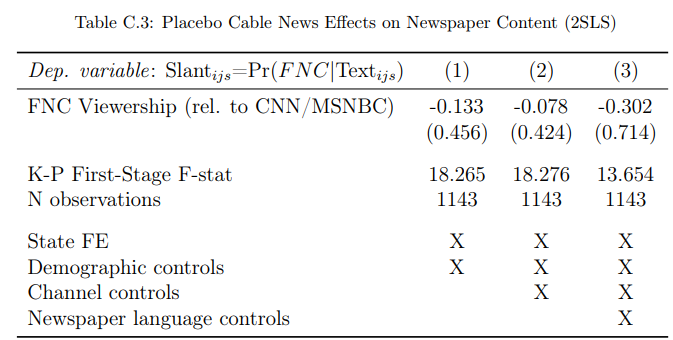
C.3. Placebo: Content similarity in 1995/96
As a placebo check, we estimate our main specifications while calculating the similarity to cable news using local newspaper articles from 1995 and 1996 (i.e., the preFNC/MSNBC era); these estimates are insignificant (Table C.3). Hence, reassuringly, there was not a pre-existing Fox-like content dimension in locations that later had a lower Fox channel position. The placebo regressions are based on fewer observations than the main results because some news outlets are not yet available in NewsLibrary in 1995 and 1996, or their circulation data is not yet available from the AAM. Our main results remain qualitatively similar and are significant if we only use the observations entering the placebo regression.
This paper is available on arxiv under CC 4.0 license.
Authors:
(1) Philine Widmer, ETH Zürich and [email protected];
(2) Sergio Galletta, ETH Zürich and [email protected];
(3) Elliott Ash, ETH Zürich and [email protected].

